Differences Between FUE vs FUT Hair Transplant
- Posted on 08 September, 2020
- Hot Topic
- By SNY Admin
The primary difference between FUT and FUE hair transplants is that in FUT, the surgeon excises a strip of donor skin from patients to remove individual follicular units to be moved to the areas plagued with hair loss. Whereas in FUE, the individual follicular units are extracted directly from the scalp.
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that extricates hair follicles from one section of the body, called the ‘donor area,’ to a thinning hair section known as the ‘recipient area.’ Primarily, the procedure treats male pattern baldness. Globally, many men, that is, greater than 60% and 50% of women suffer androgenetic alopecia and inexorable hair loss. A hair transplant can remedy the medical condition.
In 1939, Japan performed the first transplant with individual scalp hairs. Subsequently, physicians came up with the “plug” method, which is fundamentally relocating large floccules of hair. And as time went by, surgeons started using mini-and-minor-sprouts of hair on the scalp of patients.
The two principal hair transplant methods are Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT)/strip and Follicular Unit Excision (FUE) – also known as Follicular Unit Extraction. Both are effective hair restoration techniques, with a high success rate in patients. So what is the difference between them? This post will explain this.
Hair Transplant Procedures
The two most popular transplant procedures that patients go through are FUE and FUT. Both processes begin to show visible growth of hair within three to six months and a different scar. Several factors will determine the technique you choose, including:
- The thinning hair area size
- The scarring from transplant procedures
- The pattern of hair loss
- The quality and amount of donated hair
A Note on How the FUT and FUE Techniques Work
Both FUE and FUT hair transplant techniques involve placing hair grafts in small incisions in the affected scalp area. In the two procedures, the surgeon has to practice great caution in distributing and positioning the tiny incisions so that there is a seamless blend with the existing hair of patients. The operating team deploys a micro-punch tool, or implanter devices or very fine forceps to insert the grafts. The surgical team has to be careful with how they store and handle follicles to avoid damaging them and thus optimize the grafts’ survival.
Interestingly, one of the points of commonality with both techniques is the graft source. The source is the donor area- areas of the scalp where the hair is genetically determined to grow for a lifetime.
FUE-Follicular Unit Extraction
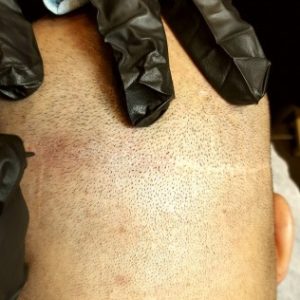
The FUE hair procedure utilizes follicle grafts from the donor areas (the head’s sides and back). For each follicle graft excision, the surgeon uses a micro-punch tool. The hair transplant scarring for this procedure is tiny and round, up to a millimeter in diameter. It depends on how the extraction of hair follicles occurs; as many as hundreds or even thousands of scars appear from the punch tool. These puncture scars may look like tiny white dots post-healing. You should know each of these follicle scars contains one to four strands.
Continually, recipient areas receive the donated hair via small incisions. You should know that this is a painstaking process that requires many hours, most likely days. It can also be done several times over within two or three months to get the best result.
Interestingly, there are no stitches needed for this procedure, and the time or recovery is usually short. It is done on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia.
FUT-Follicular Unit Transplantation
This surgery necessitates the extraction of a strip of scalp from the donor area. Typically, the donor area is on the occiput. Once the surgeon removes the strip, he or she sutures the field or donor area together. The suturing leaves a linear scar of variable lengths, predicated on the extracted strip. There are instances where the scar tissue elongates from ear to ear. The hair follicle grafts came from the scalp strip and grafted onto the recipient areas where micro-incisions are there for each hair. Ten days later, you can go and get your stitches removed. This procedure also uses local anesthesia and is done on an outpatient basis. This hair transplant surgery deploys local anesthesia, and you can get it as an outpatient. Furthermore, the FUT procedure has the chance of causing more swelling and pain than FUE, but results may vary individually.
In terms of supply, long-term donor hair will be determined by how loose or lax the scalp’s skin is and how many hair patients have per square centimeter of donor scalp. Broadly speaking, FUE vs. FUT, the FUT hair procedure grants access to a higher donor hair yield in a lifetime relative to FUE.
Pros and Cons
Both FUT and FUE processes have their pros and cons. FUT is often described as a more sophisticated technique, although they both provide superlative results. Therefore, choosing the best method or the most suitable one is mainly dependent on the patient’s specific needs and traits.
Here are some of the factors you and your surgeon will need to consider:
Pros of FUE
- There is little to no trace of scarring that is found on the scalp of patients post-recovery.
- The FUE hair procedure is suitable for patients who wish to keep short hair.
- The patients have a short recovery period (5-7 days).
Cons of FUE
- It is time-consuming, especially the time taken in the extraction of grafts.
- Concerning relative costs, FUT vs. FUE, FUE costs much more compared to FUT.
Pros of FUT
- The FUT hair procedure is excellent for patients that require a considerable amount of grafting– When it comes to FUT vs. FUE, FUT usually offers a larger yield of hair than FUE. This advantage is brilliant, especially if the patient’s main objective is to have maximum fullness when the restoration of hair.
- It can occur even with partial shaving – this means that the patient can hide the linear scar with the remaining hair.
- Shorter surgery time (FUE vs. FUT) – the FUT method hovers between 4-12 hours considering the size of the donor area and the number of grafts required in transplantation. On the other hand, FUE requires about 10 hours or more- because the donor area might require more than 2,000 grafts; in some instances, the surgery might need more than a day to complete.
- Lower price – FUT usually costs less than its counterpart FUE procedure.
- Both FUE and FUT are painless procedures, and you will only be under a local anesthetic.
Cons of FUT
- You have to cover up the linear scar because it remains visible in the donor area (contemporary techniques for sewing up the incision have diminished the scar) ‘s visibility.
- The recovery period takes longer- 10-14 days.
How Scalp Micropigmentation Can Help in FUE and FUT Scarring
Ineluctably, a hair transplant scar from hair transplant surgical techniques is an inevitable concomitant effect. Observably, a linear scar across your occiput in the back of your head is due to one of the said techniques. Transplant scars indicate that one has undergone restorative surgery, strip surgery, or the FUT procedure. The other surgical procedure is known as the FUE procedure. Regarding the FUE procedure, the scars appear as white dots in some people. One of the most important things to remember when getting a transplant surgery is the surgeon’s skill and experience, which, to a greater extent, determines the level of scarring you have.
Scalp micropigmentation (SMP) is a procedure that uses a stippling pattern tattoo that imitates hair follicles cut close to the scalp. As a relatively novel technique, scalp micropigmentation can substantially address the cosmetic issues that arise from losing hair conditions. Furthermore, scalp micropigmentation can cover up scars. The tattoo industry has undergone a cultural augmentation since the last two years of the first decade of the millennium, which made scalp micropigmentation an increasingly socially acceptable hair loss solution for tackling apropos scalp and hair challenges.
How It Is Done
Hair transplant concealment involves the insertion of numerous microdots into the scalp. Follicular units fill the scar and the surrounding areas with gaps to ensure a proper blend and concealment of the scar. The FUT procedure’s scar conceals to create an even tone at the back of the head.
Normally, after the first session, patients can perceive the difference between the fresh scar tissue and the treated scar area. The second session will make extra pigmentation to aid camouflage the scar better. Generally, after the second session of individual follicular pigmentation, the scar tissue that was apparent now matches the neighboring area’s individual follicular units.
A Note on Scars
Scarring from hair transplant procedures is inevitable. According to Scalp International Hairlines, 30% of patients opt for the scalp micropigmentation procedure to conceal scars. Scar tissue consists typically of fibrous tissue- it is the anatomy’s natural way of supplanting and healing damaged skin. A hair transplant scar situation is undesirable, which is why scar tissue remodeling and reduction where pertinent is crucial in SMP concealment. Hair transplant scars work well with SMP, but ensure you know scalp micropigmentation and hair transplant difference.
Conclusion
No matter which procedure patients go with, all of them require significant technical skills. However, what is a science without art, right? The surgeon is both scientist and artist, and in his endeavor, he or she must worry about the density, angle, and graft positioning for each unit transplantation. All the while, he is cognizant of the patient’s outward appearance- such as face and skull shape, for instance. This meticulousness matters equally despite the sort of procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is FUEMore Expensive Than Fut?
Yes, FUE is more expensive than Fut.
Which Hair Transplant Method Is Best?
The best hair transplant method is the one that will lead to a natural-looking result for patients.
What Is the Best Age To Get Hair Transplant?
The best age to get a hair transplant is 40 and above because that is typical of the time baldness starts to kick in. It is essential to understand this so that patients can get the right transplant for them.